伪汇编
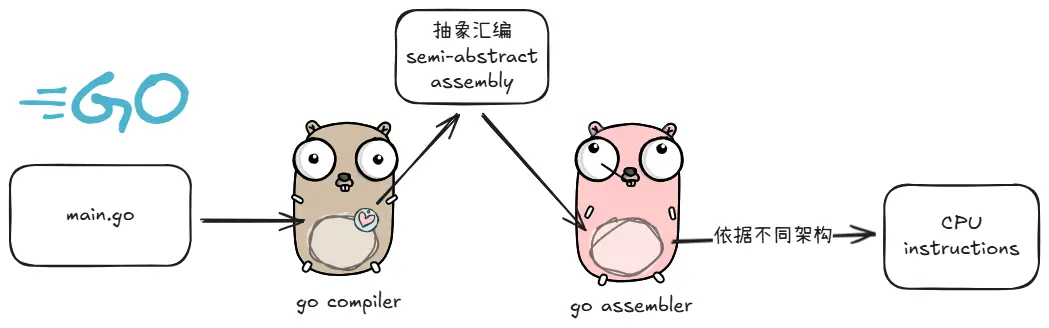 Go 汇编是抽象中间层
Go 汇编是抽象中间层
- Go 编译器输出的是一种抽象的、可移植的汇编形式
- 这种汇编不直接对应真实硬件指令
- Go 汇编器将这个"伪汇编"转换为具体硬件的机器指令
设计目标:易于移植
- 主要优势:简化 Go 语言向新架构的移植
- 只需要为新硬件实现汇编器后端,无需重写整个编译器
- 这是 Go 能快速支持多种架构的关键设计
简单示例
代码示例
package main
//go:noinline
func add(a, b int32) (int32, bool) {
return a + b, true
}
func main() { add(10, 32) }
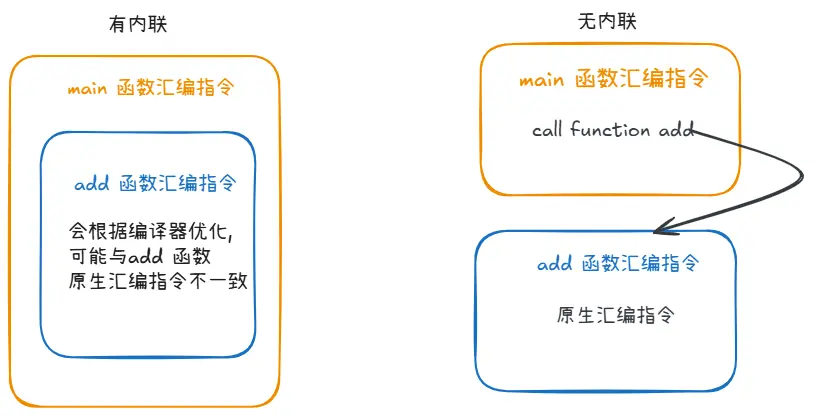
//go:noinline 即编译时采取无内联的形式, 有无内联的区别可以参照下图
编译示例
运行环境 WSL Ubuntu 24.04 LTS 64位
# -S 打印汇编指令信息 -N 关闭编译器优化
# 读者也可以不使用 -N 自行观察两种模式下编译的产物差异
w@LAPTOP-IDKREHQV:~/go-test$ go tool compile -S -N main.go
# add 函数编译指令
main.add STEXT nosplit size=51 args=0x8 locals=0x10 funcid=0x0 align=0x0
0x0000 00000 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) TEXT main.add(SB), NOSPLIT|ABIInternal, $16-8
0x0000 00000 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) PUSHQ BP
0x0001 00001 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) MOVQ SP, BP
0x0004 00004 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) SUBQ $8, SP
0x0008 00008 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) FUNCDATA $0, gclocals·g5+hNtRBP6YXNjfog7aZjQ==(SB)
0x0008 00008 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) FUNCDATA $1, gclocals·g5+hNtRBP6YXNjfog7aZjQ==(SB)
0x0008 00008 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) FUNCDATA $5, main.add.arginfo1(SB)
0x0008 00008 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) MOVL AX, main.a+24(SP)
0x000c 00012 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) MOVL BX, main.b+28(SP)
0x0010 00016 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) MOVL $0, main.~r0+4(SP)
0x0018 00024 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:3) MOVB $0, main.~r1+3(SP)
0x001d 00029 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) ADDL BX, AX
0x001f 00031 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) MOVL AX, main.~r0+4(SP)
0x0023 00035 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) MOVB $1, main.~r1+3(SP)
0x0028 00040 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) MOVL $1, BX
0x002d 00045 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) ADDQ $8, SP
0x0031 00049 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) POPQ BP
0x0032 00050 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:4) RET
# main 函数编译指令
main.main STEXT size=42 args=0x0 locals=0x10 funcid=0x0 align=0x0
0x0000 00000 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) TEXT main.main(SB), ABIInternal, $16-0
0x0000 00000 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) CMPQ SP, 16(R14)
0x0004 00004 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $0, $-2
0x0004 00004 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) JLS 35
0x0006 00006 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $0, $-1
0x0006 00006 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PUSHQ BP
0x0007 00007 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) MOVQ SP, BP
0x000a 00010 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) SUBQ $8, SP
0x000e 00014 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) FUNCDATA $0, gclocals·g5+hNtRBP6YXNjfog7aZjQ==(SB)
0x000e 00014 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) FUNCDATA $1, gclocals·g5+hNtRBP6YXNjfog7aZjQ==(SB)
0x000e 00014 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) MOVL $10, AX
0x0013 00019 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) MOVL $32, BX
0x0018 00024 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $1, $0
0x0018 00024 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) CALL main.add(SB)
0x001d 00029 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) ADDQ $8, SP
0x0021 00033 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) POPQ BP
0x0022 00034 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) RET
0x0023 00035 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) NOP
0x0023 00035 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $1, $-1
0x0023 00035 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $0, $-2
0x0023 00035 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) CALL runtime.morestack_noctxt(SB)
0x0028 00040 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) PCDATA $0, $-1
0x0028 00040 (/home/w/go-test/main.go:7) JMP 0 .....
add 函数编译解析
- 标头字段解释
TEXT main.add(SB), NOSPLIT|ABIInternal, $16-8
- main: 代表包名, 并不是 main 函数
- NOSPLIT: 表示不用进行栈溢出检测, 通常存在于没有本地变量的函数, 无需额外栈帧分配
- $16-8:
16表示分配 16 字节大小的栈帧(之后会解释 16 从哪里来),8表示参数大小位 8 字节(两个int32)
- golang 栈特性
在 golang 中栈的分配大多数情况下不通过 PUSH/POP, 而是通过改变 SP 寄存器的指针指向,即:
SUBQ $8, SP # 将 SP 指针下移, 分配额外栈空间
ADDQ $8, SP # 函数运行完成后, 将 SP 指针上移, 回收先前分配的栈空间
- 栈空间分布
了解了 golang 栈特性, 现在我们来分析示例代码 add 函数在运行时的栈空间分布
- 在 golang 编译指令中数据通过相对 SP 的位置来访问, 例如
main.a+32(SP)即 a 在当前 SP 指针 上方 32 字节处 PUSHQ BP, 即将 BP 压入栈顶, 此时 SP - 8, 再加上SUBQ $8, SP, 刚好给 add 函数分配 16 字节栈帧, 对应了$16CALL main.add(SB), 即调用 add 函数, 同时会把返回地址压入栈顶, 此时 SP - 8
综合以下代码分析
PUSHQ BP
MOVQ SP, BP
SUBQ $8, SP
...
MOVL AX, main.a+24(SP)
MOVL BX, main.b+28(SP)
MOVL $0, main.~r0+4(SP)
MOVB $0, main.~r1+3(SP)
ADDL BX, AX
MOVL AX, main.~r0+4(SP)
MOVB $1, main.~r1+3(SP)
...
可得如下栈空间分布试图
| | |
| | main.b int32 |
| | |
| +--------------------------------------+<-------+28(SP)
| main | |
| function | main.a int32 |
| stack | |
| +--------------------------------------+<-------+24(SP)
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | return address |
| | |
| | |
| | |
+------------->+--------------------------------------+<-------+16(SP)
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | BP (prev) |
| | |
| | |
| add | |
| function +--------------------------------------+<-------+8(SP)
| stack | |
| | main.~r0 int32 |
| | |
| +--------------------------------------+<-------+4(SP)
| | main.~r1 bool |
| +--------------------------------------+<-------+3(SP)
| | |
| | |
+------------->+--------------------------------------<--------SP
- 在调用者(即 main 函数)栈帧中有相应位置记录传入参数
- return address 由
CALL main.add(SB)命令压入栈中
在 Go 中,被调用函数的栈本地变量属于被调用函数的栈帧; 函数参数采用 caller-allocated 方式,由调用者在其栈帧中预留参数槽, 这些参数槽通常位于返回地址之上 当实参是调用者的本地变量时,编译器可能生成参数副本,也可能复用已有槽位,但语义上仅保证值传递,而不保证物理拷贝 读者可用以下代码自行测试
package main
//go:noinline
func add(a, b int32) (int32, bool, int32) {
var c int32 = 5
return a + b, true, c
}
func main() {
var a int32 = 10
add(a, 32)
}
stacks && splits
stacks
stack 官方源码定义
const (
// stackSystem is a number of additional bytes to add
// to each stack below the usual guard area for OS-specific
// purposes like signal handling. Used on Windows, Plan 9,
// and iOS because they do not use a separate stack.
stackSystem = goos.IsWindows*4096 + goos.IsPlan9*512 + goos.IsIos*goarch.IsArm64*1024
// The minimum size of stack used by Go code
stackMin = 2048
// The minimum stack size to allocate.
// The hackery here rounds fixedStack0 up to a power of 2.
fixedStack0 = stackMin + stackSystem
fixedStack1 = fixedStack0 - 1
fixedStack2 = fixedStack1 | (fixedStack1 >> 1)
fixedStack3 = fixedStack2 | (fixedStack2 >> 2)
fixedStack4 = fixedStack3 | (fixedStack3 >> 4)
fixedStack5 = fixedStack4 | (fixedStack4 >> 8)
fixedStack6 = fixedStack5 | (fixedStack5 >> 16)
fixedStack = fixedStack6 + 1
// stackNosplit is the maximum number of bytes that a chain of NOSPLIT
// functions can use.
// This arithmetic must match that in cmd/internal/objabi/stack.go:StackNosplit.
stackNosplit = abi.StackNosplitBase * sys.StackGuardMultiplier
// The stack guard is a pointer this many bytes above the
// bottom of the stack.
//
// The guard leaves enough room for a stackNosplit chain of NOSPLIT calls
// plus one stackSmall frame plus stackSystem bytes for the OS.
// This arithmetic must match that in cmd/internal/objabi/stack.go:StackLimit.
stackGuard = stackNosplit + stackSystem + abi.StackSmall
)
- Go 为所有系统统一规定了 goroutine 的最小初始栈大小为 2KB;在 Windows、Plan9、iOS 等系统上,会额外预留 stackSystem 空间用于 OS 信号处理,而 Linux 不需要该预留
- stackNosplit 表示一条连续的 NOSPLIT 函数调用链在最坏情况下允许使用的最大栈空间
- stack.lo + stackGuard 是栈警戒线:普通函数若 SP 低于该值将触发 morestack 进行栈扩容,而 NOSPLIT 函数必须保证永不触达,否则直接崩溃
splits
Go 的栈分裂机制并不是运行时“自动感知”的,而是依赖编译器在函数入口插入显式的栈检查代码;NOSPLIT 本质上是一种对编译器的安全承诺:该函数及其调用链在任何情况下都不会耗尽预留的 nosplit 栈空间
goroutine 官方源码定义
type g struct {
// Stack parameters.
// stack describes the actual stack memory: [stack.lo, stack.hi).
// stackguard0 is the stack pointer compared in the Go stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard normally, but can be StackPreempt to trigger a preemption.
// stackguard1 is the stack pointer compared in the //go:systemstack stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard on g0 and gsignal stacks.
// It is ~0 on other goroutine stacks, to trigger a call to morestackc (and crash).
stack stack // offset known to runtime/cgo
stackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblink
stackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink
......
}
stackguard0是普通 Go 函数使用的栈警戒线,用于可增长的用户 goroutine 栈,触达时会调用 morestack 扩容,并可被设置为 StackPreempt 以触发抢占stackguard1是 //go:systemstack 函数使用的栈警戒线,在 g0 / gsignal 栈上用于防止 system stack 被踩穿,在普通 goroutine 上被置为 ~0 以强制 systemstack 路径崩溃,从而保证 system stack 永不扩栈
| |<---------stack.hi
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
+-------------------------------------------<----------SP
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
+-------------------------------------------+<---------stackGuard0(stack.lo + stackGuard)
| |
| |
| stackSmall |
| |
+-------------------------------------------+
| |
| stackNosplit |
| |
| |
+-------------------------------------------+
| |
| stackSystem |
| Windows: 4096 bytes |
| Plan9: 512 bytes |
| iOS/ARM64: 1024 bytes |
| |
| |
| |
+-------------------------------------------+<--------stack.lo
Prologue (序幕)
位于示例 main 函数汇编指令开头 作用:检查当前 goroutine 的栈是否还够用
CMPQ SP, 16(R14)
PCDATA $0, $-2
JLS 35
CMPQ SP, 16(R14)
- CMPQ:比较两个 64 位值(无符号比较)
- SP:当前栈指针(当前函数栈帧的底部,向下增长)
- 16(R14):R14 寄存器指向当前 goroutine 的 g 结构体,偏移 16 字节处是 g.stackguard0 → 16(R14) == g.stackguard0(栈保护边界,guard 值)
- 含义:比较 SP 是否 ≤ g.stackguard0
- 如果 SP ≤ guard → 栈已经用得太深(接近或进入保护区),需要扩容
- 如果 SP > guard → 栈还有足够空间,继续执行
JLS 35
- JLS:Jump if Less or Same(小于或等于则跳转)
- 跳转目标:地址 35(0x0023),那里是 CALL runtime.morestack_noctxt(SB)
- 条件:SP ≤ g.stackguard0 时跳转
- 如果不跳转(栈足够)→ 继续执行 PUSHQ BP、SUBQ $xx, SP 等正常函数序言
Epilogue (结尾)
位于示例 main 函数汇编指令结尾
CALL runtime.morestack_noctxt(SB)
JMP 0
- CALL runtime.morestack_noctxt(SB)
- 核心:调用运行时栈扩容函数
- morestack_noctxt:无上下文版本(no context),表示不携带调用者寄存器上下文(因为是从栈检查跳转来的)
- 功能:分配新栈(通常翻倍)、拷贝旧栈内容、更新 g.stack、g.stackguard0 等,然后返回
- JMP 0
- 无条件跳转回函数开头(地址 0x0000)
- 原因:栈扩容后,原 SP 已失效,需要重新执行栈检查(CMPQ),确认新栈足够大。如果仍不够(极罕见),会再次调用 morestack